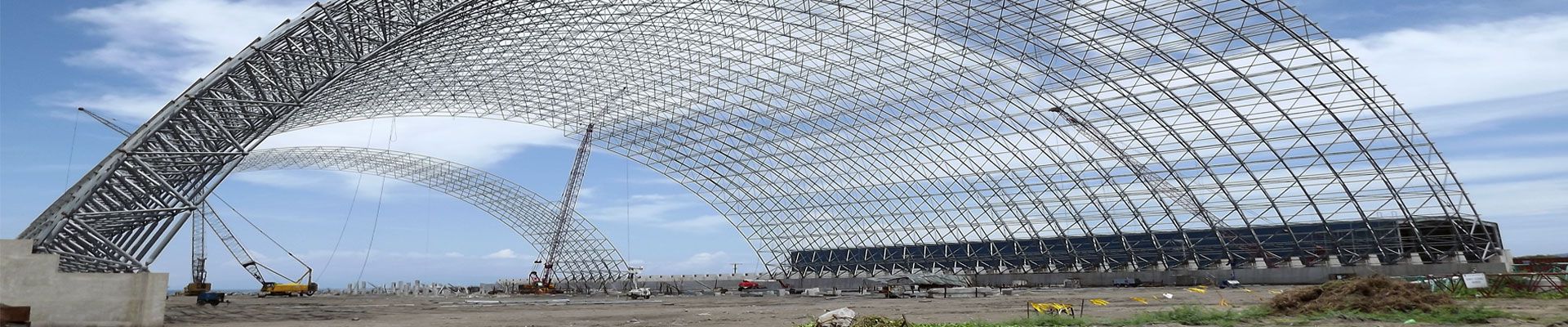
4.Node Production
Welding ball node production:
material: according to the design size, cut steel plate to make the hemisphere of welding ball. The thickness of the steel plate should be determined according to the factors such as the span and load of the space frame, generally 6 – 20mm.
Pressing the hemisphere: the cut steel plate will be pressed or stamped into the shape of the hemisphere on the press. During the pressing process, the precision of the mold and pressing pressure should be controlled to ensure that the radius of curvature and wall thickness of the hemisphere is uniform.
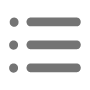
Welding hemispheres: two hemispheres are welded together to form a complete welded sphere. Welding should adopt suitable welding process (such as submerged arc welding, carbon dioxide gas-shielded welding, etc.) to ensure the welding quality, and the weld should be subjected to appearance inspection and non-destructive testing (such as ultrasonic flaw detection) to ensure that there are no defects such as cracks and porosity.
Bolt ball node production:
Forging blanks: make bolt ball blanks by forging process, the size of blanks should be slightly larger than the size of the finished product, leaving a margin for subsequent processing. Forging can improve the internal organization of steel, improve its mechanical properties.

Machining: The blank is mechanically processed, including turning, drilling and other processes. Drill holes in the bolt ball for the installation of high-strength bolts, screw holes in the position of the high precision requirements, adjacent screw holes center distance deviation is generally controlled in the range of ± 0.15 – 0.3mm. The surface of the processed bolts should be smooth, without cracks, sand holes and other defects.
5.Assembly of Space Frame
Assembling unit: the processed rods and nodes are assembled into small assembling unit in the factory, and the size and form of the small assembling unit are determined according to the characteristics of the space frame structure and the transportation and installation conditions. For example, several neighboring rods and nodes can be assembled into triangular, quadrilateral and other small units. In the process of assembly, special jigs and fixtures should be used to ensure the connection accuracy of rods and nodes, such as the angular deviation of the axes of rods and the positional deviation of the center of the nodes should be controlled within the permissible range.
Assembling of middle splicing unit (if necessary): For some large-scale space frame structures, on the basis of small splicing unit, several small splicing units will be further assembled into middle splicing unit in the factory, in order to reduce the workload of on-site installation. The assembly of the center unit should also be strictly controlled to ensure that the geometry and size of the unit meet the design requirements.
Total assembling: small assembling unit or middle assembling unit is transported to the construction site for total assembling. Total assembly can be used overhead bulk method, strip and block installation method, overall lifting method and other installation methods. In the process of total assembly, the geometric size and spatial position of the space frame should be checked while installing, and the overall accuracy of the space frame should be ensured by adjusting the length and installation position of the bars and other measures. For example, the span deviation of the space frame should not exceed ±30mm, and the height deviation should not exceed ±L/2000 (L is the span of the space frame).

6.Quality Inspection and Acceptance
Appearance Inspection: Carry out comprehensive appearance inspection on the completed space frame structure, check whether there are defects such as damage, deformation, rust and corrosion on the surfaces of rods and nodes, whether the appearance of weld meets the requirements (e.g. residual height, width uniformity, etc. of the weld), and whether the bolting connection is firm with any loosening phenomenon.
Dimensional accuracy check: use measuring tools (such as total station, steel ruler, etc.) to check the geometric dimensions of the space frame, including span, height, space size, etc. The check results should be in line with the design and specification requirements.
Non-destructive testing: carry out non-destructive testing on the welds in the key parts, such as ultrasonic flaw detection, magnetic particle flaw detection or ray detection, etc., to detect whether there are defects inside the welds. For welded ball nodes, 100% NDT shall be carried out for primary and secondary welds.
Load test (if necessary): For some important or large-scale space frame structure, it may be necessary to carry out load test to simulate the actual use of the load, check the load carrying capacity of the space frame, deformation, etc. The load test can be divided into static load test, static load test, static load test, static load test, static load test and static load test. Load test can be divided into static load test and dynamic load test, through applying graded load on the space frame, measuring its deformation and stress change, and verifying whether the space frame structure meets the design requirements.







 About Us
About Us 2025-05-05
2025-05-05


