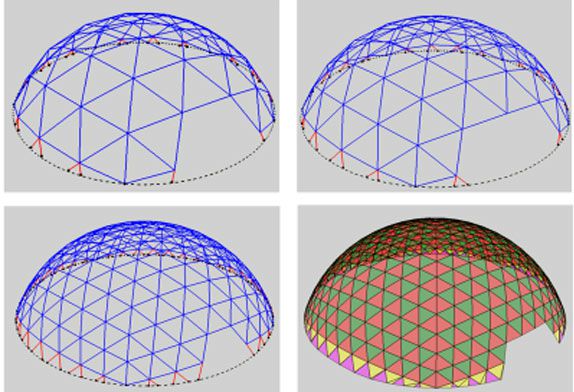
The support system is to directly transmits various loads borne by the glass surface to the main structure of the building, so it is the main force-bearing member, and the structural form and material are generally selected according to the building shape and the load it bears. Considering the enhancement of permeability, in order to increase the degree of natural lighting, point glass technology is often used as the roof. At the same time, the support structure of the pointed glass is diverse, the design is flexible, and the construction is convenient, which is conducive to the design of a unique building roof. Point glass roofs are divided into four types according to the supporting structure: all-glass point glass roofs, point glass roofs supported by arches, beams or rigid frames, point glass roofs supported by cable trusses, and space bar systems or point glass roofs with cable systems.
1. Full glass structure point glass roof
The all-glass point-type glass roof refers to the structure that mainly consists of glass components to support the roof, and the roof glass is connected by point-type steel components. Among them, glass is the main load-bearing structure, and this structural system requires high glass strength.
It is very difficult to simply use glass as a beam system to support the roof of the building because the tensile properties of glass are very poor. In the early practice of point glass building, there were attempts, but it proved that this kind of structure can only be applied to small spans and cannot be used for a long time.
How to overcome the problem of poor tensile properties of glass and convert it into a more suitable pressure has become the main problem of this type of structural design. For example, a point-type glass roof with an all-glass structure can adopt a very simple and practical structure, that is, apply the principle of folded plate structure to design. The glass plates are arranged to support each other at a certain angle, and the self-weight of the glass is borne by the compressive capacity of the glass itself, which reduces the tensile force on the individual glass, thus better solving this problem. The supporting structure of the roof is a row of bent steel pipes with a distance of 2m from each other, and the cantilever part extends 3.5m outward. The glass frames are mounted on steel pipes at an angle of 46° to each other. The upper and lower parts connected by the two pieces of glass are supported by angle steel, and point-type components protrude from the angle steel to fix the glass. For safety reasons, the glass is made of laminated safety glass consisting of pre-stretched safety glass.
2. Point glass roofs supported by arches, beams, or rigid frames
The point-type glass roof supported by arches, beams or rigid frames refers to the main support structure with arches, beams, or rigid frames, on which point-type components are connected to support or hang the glass roof. If the glass is directly used as a beam, arch, or part of these structural systems, it is the main load-bearing structure of the glass. But in most of the current cases, based on the mechanical properties of glass, glass is basically used as a secondary load-bearing structure. Each glass arch is composed of 3 pieces of fish-belly flat glass. There is a cable at the bottom of the glass, which connects the three hinge points on the entire arch, and can partially bear the tension to prevent the glass from breaking due to excessive tension. The 9 steel pipes running along the lengthwise direction of the inner edge are not only the stable support of the horizontal glass arch but also the connecting support body of all the claws. The glass arch is made of laminated safety glass, consisting of 10mm thick pre-stretched safety glass and 15mm single-piece safety glass. The roof glass is double-glazed, the upper layer is float glass and the lower layer is laminated safety glass. Each glass is 2.50×0.80m, supported by 6 points.
3. Under-tensioned cable-type truss support-point glass roof
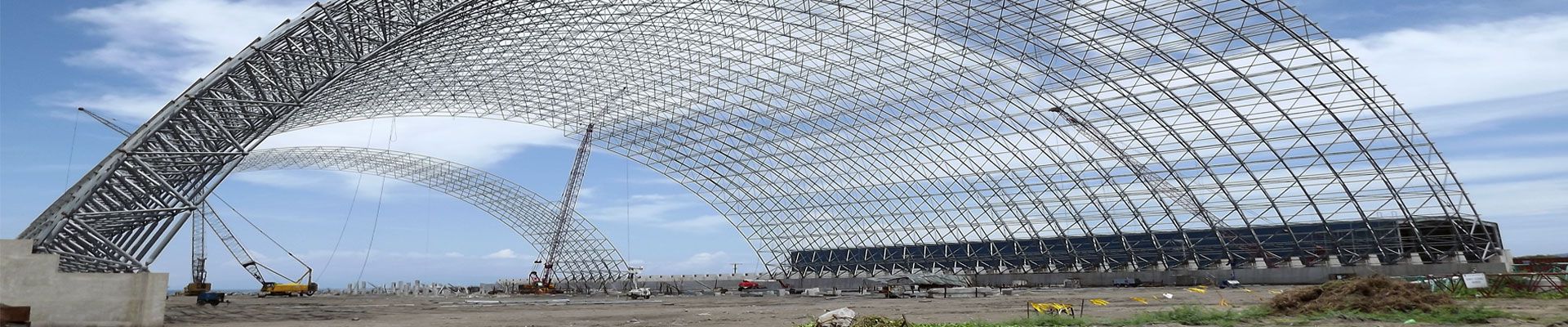
The under-tensioned cable truss supporting point glass roof refers to the part of the middle and lower tie rods of the truss composed of steel cables and steel rods, or completely composed of steel cables, and steel rods or glass. This cable truss system connects the glass with point members. The supporting point glass structure of the cable-type truss can be the main load-bearing of the glass, or the secondary load-bearing of the glass. If glass is used as part of struts or strut members, the truss structure is a system in which glass is used as the main load-bearing structure. This glass or steel rod is used as the compression rod in the truss system, which is a special form of truss structure. At the same time, its slender rods and exquisite form can be well combined with point glass technology, thus showing the characteristics of mechanical aesthetics and good optical permeability of point glass roofs. It is a point glass roof type that has been widely used in recent years.
4. point glass roof with rod or cable system
The point glass roof of space bar or cable system is a roof form formed by combining space structure and point glass technology. Point-type glass technology has a good combination with space structure. For example, the hinge of point-type components can well meet the requirements of deformation of flexible space structures, and the glass is connected by a single piece of vertex-type components, which is simple in construction and maintenance. It has nothing to do with the overall structure. In addition, the glass can be used as the compression bar of the system to bear part of the load, so as to reduce the number of additional components and increase the transparency of the roof. The point-type glass roof of the spatial rod or cable system is therefore very popular in applications with large spans. Fig. 8 is the Louvre Pyramid in France, a hexahedron composed of 4 steel pipes and 8 steel cables is suspended by 4 cable trusses drawn in the diagonal direction of the outdoor floor opening. A total of 7 layers of hexagonal cable loops are connected to the fixed points of the cable truss and the hexahedron and the midpoint of the steel pipe. A huge and complex cable net system constitutes the main structure of this pyramid. Claws protruding from the cable nets are fixed at the corners of each glass. In order to avoid the uneven surface of the pyramid, the prestress of all cables and rods has been carefully calculated, just enough to bear the self-weight of the glass.







 About Us
About Us 2023-02-06
2023-02-06


