1 Overview
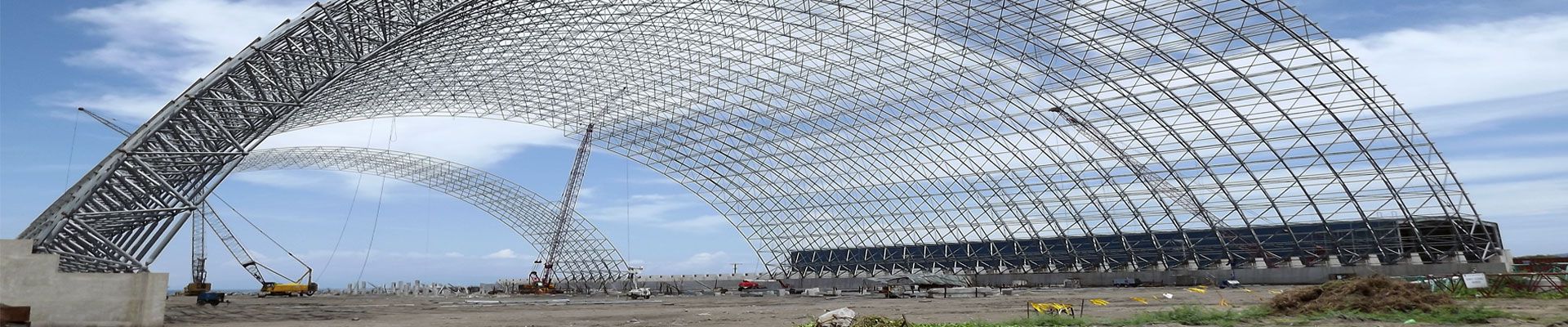
In recent years, long-span structures have been widely used not only in sports buildings, but also in various commercial buildings (such as supermarkets, warehouses and workshops), and the application of long-span structures in building structures in China is also increasing. For example, in the reconstruction and expansion project of wuchang railway station, the west station building with a total length of 245.8m, the roof of the canopy without platform columns, the roof of the main station building and the elevated waiting room of suzhou railway station all adopt the vertical and horizontal steel truss structure system, except In addition to continuing to be widely used in these fields, there are also some super-large structures, such as the hangar of Singapore Changi Airport and the departure hall of Osaka International Airport; there are also light-duty long-span structures, such as pedestrian bridges and crane structures; other special-purpose structures Structures such as antenna masts and space launch pads, etc. In these projects, the planar truss system can show the beautiful shape and smooth lines of its structure, and it is easier to realize the designer’s pursuit of architectural art, and it has been favored by people. However, during the construction process, the construction is often difficult due to the large span of the structure, so the requirements for the design and construction of the scheme are getting higher and higher. Some construction methods are briefly described as follows:
2 Selection of construction method
There are basically two types of construction and installation of large-span space structures, namely high-altitude assembly and ground assembly and lifting. High-altitude assembly is to solve the problem of how to effectively construct at high altitude, while the latter emphasizes the machines and techniques that should be used. The construction methods of traditional large-span structures generally include: high-altitude bulk method, strip or block installation method, high-altitude sliding method, overall hoisting method, overall lifting method, and overall jacking method. However, due to the complex shape of modern large-span structures and the extensive use of new materials and technologies, traditional installation methods often fail to complete the task smoothly, and sometimes even fail to complete the task. Through a large number of engineering practices, many innovative construction technologies have emerged at home and abroad, such as high-altitude curved sliding technology, reticulated shell structure folding and unfolding overall lifting technology, and sliding frame method construction technology. The installation method of modern long-span structures is often an ingenious combination or re-creation of several basic methods. At the same time, due to the rapid development of mechanical equipment, calculation theory and computer technology, it provides strong support for the innovation of installation methods of large-span structures, making the installation methods of large-span structures more diversified.
3 selection of rods
3.1 Material selection of rods: Q235 and Q355 are mostly used for trusses, and the cross-sectional forms mainly include round tubes, single angle steels, double angle steels, H-shaped steels, square tubes, etc. At present, the most widely used in China are round steel pipes and double angle steel rods.
3.2 Requirements for bar section:
(1) During construction, it is necessary to effectively select the section of the rod. The round steel should not be smaller than 48mm×3mm, and the angle steel should not be smaller than L45mm×3mm or L56mm×36mm×3mm.
(2) When selecting the section, it should be avoided that the chord of the largest section and the web member of the smallest section intersect at one node
(3) The selected cross-sectional specifications of the truss structure should not be too many to facilitate processing and installation .
(4) The rod should choose a section with a thinner wall thickness in order to obtain a larger radius of gyration, which is conducive to the stability of the pressure rod.
(5) Select steel models commonly available in the market .
(6) Considering the influence of the negative tolerance of the member material, it is advisable to leave appropriate room for the design and construction of the 4 nodes .
4.1 Requirements for node design: safe and reliable, clear and concise force transmission; simple structure, convenient manufacture, easy installation; less steel consumption, low cost; reasonable structure, so that the stress state of each node conforms to the design calculation assumptions, so as to avoid additional Eccentric moment.
4.2 Connection form of nodes:
(1) The first is bolt connection: that is, a round hole is directly opened on the upper flange of the roof beam or the support, and the oval hole on the connecting plate at the end of the truss is generally connected by ordinary M16 bolts; the second is welding connection: that is, the connecting plate at the end of the truss It is directly located on the upper flange or support of the roof beam, and is manually welded on site, using four-sided surrounding welding, and the weld height is generally 8mm.
(2) Welded connection: The butt welds of structural members are full penetration welds according to the requirements, and should meet the requirements of Class 2 welds. On-site welding adopts manual arc welding. Welders hold certificates and have many years of inspection. On-site welders must be trained and explained. Welding machines, electrode ovens, grinding wheel grinders, and carbon arc gouging must be adequately equipped.
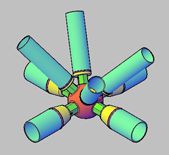
Before welding: the welding rod should be baked, and the inner and outer walls of the groove should be carefully cleaned within 15-20mm. Remove oil, rust, and dirt, and check whether the groove angle, blunt edge, and clearance are consistent. The truss adopts the intersecting joints directly welded between the web and the chord. The connection with the branch pipe is in the form of intersecting nodes such as T, Y, K, etc., and the end of the branch pipe is a saddle-shaped curve.
When welding, the swing range should be small, and according to the requirements of the process evaluation documents, multi-pass and multi-layer welding should be carried out to strictly remove the welding slag, slag inclusions and oxides of the weld bead and weld layer.







 About Us
About Us 2023-06-26
2023-06-26


